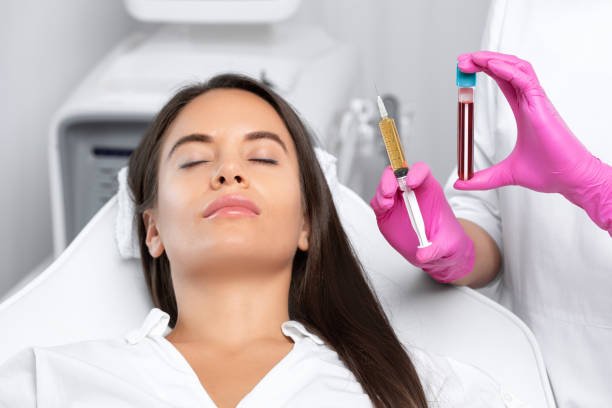
PRP
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) is a regenerative treatment that utilizes the patient's own blood to encourage healing and tissue regeneration. The process involves extracting platelets, concentrating them, and then injecting them into the targeted area. PRP has a wide range of applications, including in sports medicine, orthopedics, dermatology, and hair restoration. It is believed to stimulate collagen production, enhance tissue repair, and accelerate healing. With its minimally invasive nature, PRP has gained popularity for its potential to effectively promote natural healing and rejuvenation.
Process of PRP
The process of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) typically involves the following
steps:
- Consultation:
The first step in the PRP treatment process is a consultation with a healthcare professional to assess whether PRP is appropriate for the patient's specific condition or needs. This helps ensure that the treatment will be effective and tailored to the individual’s goals.
- Blood Draw: A
A small amount of the patient’s blood is drawn, typically from their arm, much like a routine blood test.
-
Centrifugation: The blood sample is placed in a centrifuge, which spins it at high speeds to separate the various components of the blood, concentrating the platelets for the PRP treatment.
-
Platelet Separation: During the centrifuge process, the platelets are separated from the other blood components, resulting in a concentrated platelet-rich plasma (PRP) that is ready for use in the treatment.
- Injection or Application: The concentrated PRP is then injected directly into the targeted area, such as joints, tendons, or the scalp for hair restoration. In some cosmetic procedures, it may also be applied topically to promote skin rejuvenation.
- Recovery and Follow-up: After PRP treatment, patients may experience mild soreness or discomfort for a short period, typically lasting only a few minutes. Rest and adherence to any specific post-treatment instructions provided by the doctor are recommended. Follow-up appointments may be scheduled to monitor progress and assess if additional treatments are necessary for optimal results.
